Parts of a GTPv1 network
A sample GTP network consists of the end handset sender, the sender’s mobile station, the carrier’s network including the SGSN and GGSN, the receiver's mobile station, and the receiver handset.
When a handset moves from one mobile station and SGSN to another, the handset’s connection to the Internet is preserved because the tunnel the handset has to the Internet using GTP tracks the user’s location and information. For example, the handset could move from one cell to another, or between countries.
The parts of a GPRS network can be separated into the following groups according to the roles of the devices:
- Radio access to the GPRS network is accomplished by mobile phones and mobile stations (MS).
- Transport the GPRS packets across the GPRS network is accomplished by SGSNs and GGSNs, both local and remote, by delivering packets to the external services.
- Billing and records are handled by CDF, CFR, HLR, and VLR devices.
GPRS networks also rely on access points and PDP contexts as central parts of the communication structure. These are not actual devices, but they are still critical .
These devices, their roles, neighboring devices, the interfaces and protocols they use are outlined in the following table.
Carrier network showing the interfaces used (GTPv1)
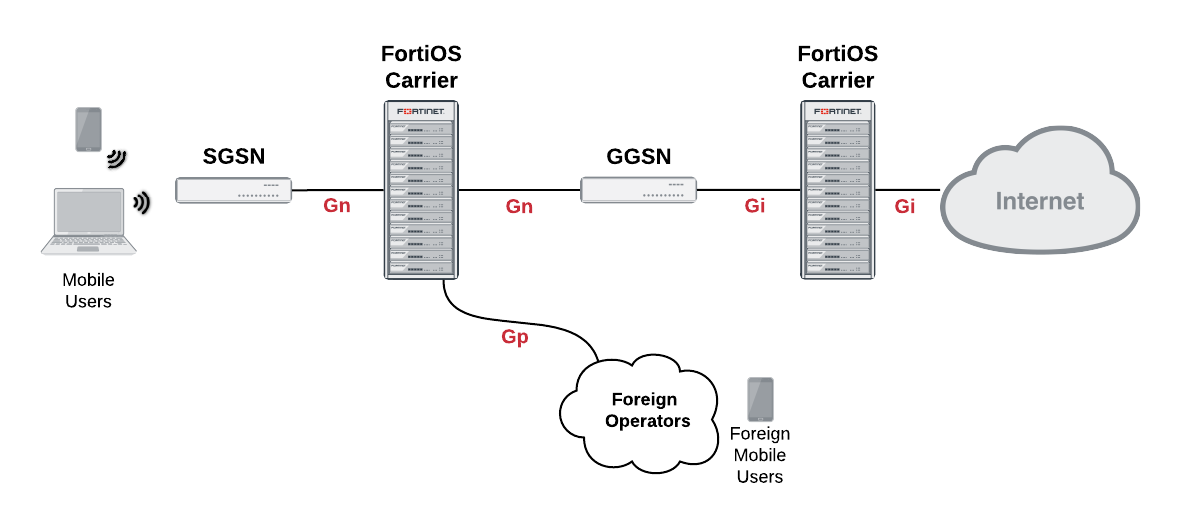
Devices on a GTPv1 network
| Device role | Neighboring Devices | Interfaces used | Protocols used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile Users | Mobile Stations (MS) | Radio Access Technology (RAT) | |
| Mobile Stations (MS) | Mobile Users, SGSN | Gb | IP, Frame Relay |
| SGSN (local) | MS, SGSN (local or remote), GGSN (local and remote), CDR, CFR, HLR, VLR | Ga, Gb, Gn, Gp, Gz | IP, Frame Relay, GTP, GTP’ |
| SGSN (remote) | SGSN (local) | Gn | GTP |
| GGSN (local) | SGSN (local or remote), GGSN (local and remote), CDR, CFR, HLR, VLR | Ga, Gi, Gn, Gp, Gz | IP, GTP, GTP’ |
| GGSN (remote) | SGSN (local), WAP gateway, Internet, other external services | Gi, Gp | IP, GTPv1 |
| CDR, CFR | SGSN (local), GGSN (local) | Ga, Gz | GTP’ |
| HLR, VLR | SGSN (local), GGSN (local) | Ga, Gz | GTP’ |

