By default, the FortiGate uses the certificate named Fortinet_GUI_Server for HTTPS administrative access. This certificate is generated and signed by the built-in Fortinet_CA_SSL certificate, which dynamically updates the SAN field of the Fortinet_GUI_Server certificate with the IP addresses of all interfaces enabled for HTTPS. After installing the Fortinet_CA_SSL CA certificate on a PC, administrators can access the FortiGate GUI through a browser without any warnings.
How the certificate works
The Fortinet_GUI_Server certificate is generated by the built-in certificate authority (CA) with the Fortinet_CA_SSL certificate, which is unique to each FortiGate. This CA certificate is also used in SSL deep inspection. When the Fortinet_GUI_Server certificate is generated, the SAN (Subject Alternative Name) extension field is populated with the IP addresses of all physical and logical (VLAN, loopback, and so on) interfaces enabled for HTTPS. It is also populated with the management IP address whenever this field is an IP address and not an FQDN. If there are any changes to the IP addresses on the interface or management IP, the Fortinet_GUI_Server certificate is updated and regenerated with the new IP. If the Fortinet_CA_SSL certificate itself is updated, the Fortinet_GUI_Server certificate is regenerated.
Because the root CA is not a public CA, the Fortinet_CA_SSL CA certificate must be installed in the trusted certificate store on the client PC in order for the trusted certificate chain to be recognized by a browser. This certificate can be downloaded from the FortiGate in several ways.
|
|
The Fortinet_GUI_Server certificate can only be used for HTTPS administrative access. It cannot be used anywhere else. |
Example
The HTTPS server certificate can be configured in the GUI or CLI.
To configure the HTTPS server certificate in the GUI:
-
On an administrative PC, log in to the FortiGate GUI and go to System > Settings.
-
In the Administration Settings section, set the HTTPS server certificate to Fortinet_GUI_Server.
-
Download the Fortinet_CA_SSL certificate using one of the following methods:
-
On the System > Settings page, click Download HTTPS CA certificate (below the HTTPS server certificate option).
-
Go to System > Certificates. In the Local CA Certificate section, select Fortinet_CA_SSL, and click Download.
-
Go to Dashboard > Status. In the Administrator widget, click Download HTTPS CA certificate.
-
-
Install the certificate in the PC’s trusted certificate store. Refer to your OS documentation if needed.
-
Reload the FortiGate GUI. The browser now trusts the certificate and does not display a certificate warning.
-
If you are connecting to the FortiGate over DNAT or port forwarding, the certificate needs to add the NATed management IP into the SAN field so that the browser does not display a warning about an invalid CN. Configure the management IP in the global settings:
config system global set management-ip <IP_address> end
To configure the HTTPS server certificate in the CLI:
-
Configure the HTTPS server certificate:
config system global set admin-server-cert Fortinet_GUI_Server end -
Download the Fortinet_CA_SSL certificate on the administrative PC through TFTP:
# execute vpn certificate local export tftp Fortinet_CA_SSL cer <file_name> <server_IP> Done.
To verify the connection:
-
Access the FortiGate from a browser and verify the certificate information. For example, in Chrome:
-
In the left side of the address bar, click the icon to view the site information.
-
Click Certificate.
-
Click the Details tab.
-
Locate the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field, and note the IP addresses that are listed (1.1.1.1).
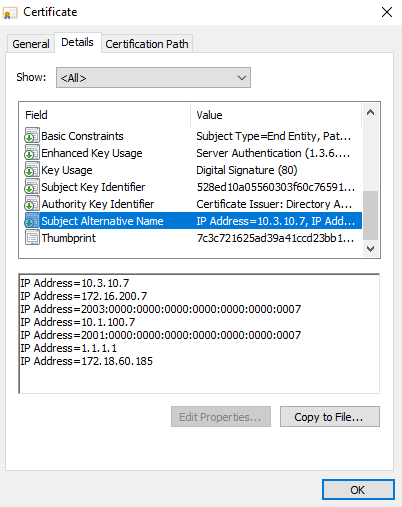
-
Click OK.
-
-
In FortiOS, change one of the interface addresses. In this example, the port11 address is changed from 1.1.1.1 to 3.3.3.3.
-
Reload the browser and review the certificate information again. The IP 1.1.1.1 in the SAN field is updated to 3.3.3.3.
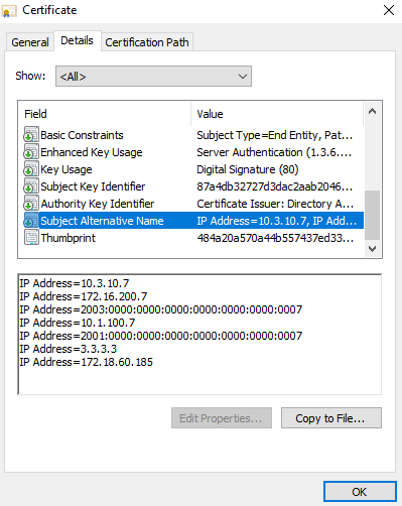
-
In FortiOS, go to System > Certificates and double-click Fortinet_GUI_Server to view the Certificate Details.
-
At the bottom of the pane, the X509v3 Subject Alternative Name field displays the IP addresses from the certificate.
-
Verify the logs when the certificate is regenerated:
# execute log filter category 1 # execute log display 12 logs found. 10 logs returned.
1: date=2022-06-23 time=09:11:44 eventtime=1656000704674434910 tz="-0700" logid="0100022205" type="event" subtype="system" level="information" vd="root" logdesc="Certificate succeed to auto-generate" user="system" action="certificate-generate" status="successful" name="Fortinet_GUI_Server" msg="Successfully generated GUI management cert"
2: date=2022-06-23 time=09:11:44 eventtime=1656000704674432668 tz="-0700" logid="0101041986" type="event" subtype="vpn" level="information" vd="root" logdesc="Certificate regenerated" action="info" user="N/A" ui="forticron" name="Fortinet_GUI_Server" msg="A certificate is regenerated" cert-type="Local" status="success"
3: date=2022-06-23 time=09:11:31 eventtime=1656000691825397831 tz="-0700" logid="0100044547" type="event" subtype="system" level="information" vd="root" logdesc="Object attribute configured" user="admin" ui="ssh(172.16.200.254)" action="Edit" cfgtid=35782662 cfgpath="system.interface" cfgobj="port11" cfgattr="ip[1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0->3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0]" msg="Edit system.interface port11"

