Appendix G : WinRM configuration for Windows server
WinRM is needed for agentless RDP session log retrieving.
Use the commands as shown below to enable WinRM and set authentication on the target Windows servers.
- Quick setup with script from FortiSRA
- Executing the script on the sever with administrative privileges
- Configuring WinRM on the server manually
- Creating a privileged account
To setup WinRM on a Windows server, you can copy the WinRM setup script (recommended) from FortiSRA and execute the script on the Windows server or do it manually.
Quick setup with script from FortiSRA
- Go to Secrets > Secrets.
- From the list, double-click to open the secret.
- Click WinRM Setup Scripton the right to open the script.

- Click Download script to download the script to your management computer. Alternatively, click Copy script to copy the script.
Executing the script on the sever with administrative privileges
To execute the script on the server with administrative privileges:
- Before executing the scripts on a newly installed machine or one that has never been configured for WinRM, please initiate winrm qc first in PowerShell.
- Run the scripts in PowerShell with administrative privileges using the following command:
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File auto_winrm.ps1
Alternatively, use the following command:
powershell.exe auto_winrm.ps1

- Choose the correct IP address as the hostname if the computer is not part of a domain. Otherwise, it uses the FQDN as the hostname.
- Choose if you want to configure HTTP listening for WinRM.

- Choose if you want to configure HTTPS listener for WinRM.

- If HTTPS is selected and there are already certificates installed, choose the one by index or enter
0to create a self-signed certificate.
The firewall rules for listeners is enabled and the list of all the listeners is displayed.
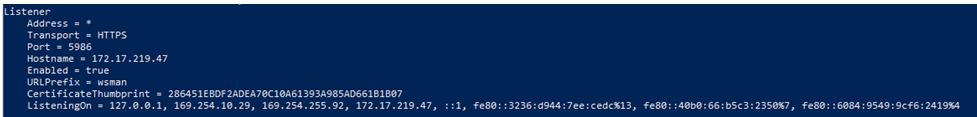
- Finally, choose if you want to enable Event log policy for RDP log retrieval feature.

Configuring WinRM on the server manually
Alternatively, you can configure WinRM manually.
To configure WinRM on the server manually:
- Open the Windows PowerShell console as an administrator and enter the following command:
winrm quickconfig
The command enables WinRM service with default setting.
- If WinRM over HTTPS is required for enhanced security, add an HTTPS listener:
- If the server has already been issued a certificate in the local certificate store, use the following command:
Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:\LocalMachine\My
This lists all the certificates in
Cert:\LocalMachine\My.Choose one and copy the thumbprint for later use.
- If the server needs a self-signed certificate, use the following command:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -Subject 'CN=<windows host name>' -TextExtension '2.5.29.37={text}1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1'Replace
<windows host name>with the actual hostname (FQDN or an IP address of the server).After running the above command, the result is displayed with the thumbprint.

- Add an HTTPS listener using the following command:
winrm create winrm/config/Listener?Address=*+Transport=HTTPS '@{Hostname="<windows host name>"; CertificateThumbprint="<thumbprint received by New-Self Signed Certificate>"}'Replace
<windows host name>with the one used in step b.Replace the
<thumbprint received by New-Self Signed Certificate>with the thumbprint from step a or b.
- If the server has already been issued a certificate in the local certificate store, use the following command:
- Use the following command to see if everything works correctly:
winrm enumerate winrm/config/listener
The above command should display the corresponding listener in the console.
- Configure the firewall rules for WinRM:
WinRM traffic (5985 for HTTP, 5986 for HTTPs) can be blocked by default on some Windows servers or cloud platforms. Ensure that the WinRM traffic is allowed for RDP log retrieving.
Enabling Windows Remote Management
- On the target Windows server, go to Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Defender Firewall.

- From the menu on the left, select Advanced settings.
- In the User Account Control dialog that opens, click Yes.
A new window opens.

- From the menu on the left, select Inbound Rules.
- In the Inbound Rules window, according to your network topology, right-click Windows Remote Management and select Enable Rule.
- On the target Windows server, go to Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Defender Firewall.
- Audit policy setting for RDP log retrieving:
- Log in to the Windows machine to configure the policy as an administrator.
- Go to Control Panel > System and Security.
- Click Administrative Tools and in the new window that opens, double-click Local Security Policy.
- In the the User Account Control dialog that opens, click Yes.
The Local Security Policy window opens.

- From the navigation pane on the left, expand Local Policies > Audit Policy.

- For the event filter profile that applies to the privileged account secret on FortiSRA:
- If Process Log is set to Monitor, set Audit process tracking as success and failure by right-clicking Audit process tracking, selecting Properties, selecting Success and Failure, and clicking OK.
- If Filesystem Log is set to Monitor, set Audit object access as success and failure by right-clicking Audit object access, selecting Properties, selecting Success and Failure, and clicking OK.

When you enable the policy to audit object access events, you must specify which files, folders, and user actions are logged.
You must be specific with the setting to avoid excessive logging.
- If User Management Log is set to Monitor, set Audit account management as success and failure by right-clicking Audit account management, selecting Properties, selecting Success and Failure, and clicking OK.
- Log in to the Windows machine to configure policy and administrator privileges.
- On the Windows machine, open File Explorer, right-click the file you intend to set the auditing policy for, and select Properties:
- Go to the Security tab, click Advanced.
- Go to the Auditing tab, click Continue.
- In the User Account Control dialog, click Yes.
- Click Add.

The Add button is labelled Edit on Windows 8.
- In the new window that opens, click Select a principal.
- In Select User, Computer, Service Account, or Group, click Advanced.
- Select users whose access to the file you want to monitor.
- Click OK.
- In the Permissions tab, set the permission for each of the user you have added.
- Click OK.
- Click OK.
The configuration is now complete. Windows will generate audit events when the users you have specified takes actions on the files or folders for which you have set up audit policies.
Creating a privileged account
We create a new user belonging to the administrators groups.
To create a privileged account:
- Go to Control Panel > System and Security.

- Click Administrative Tools.
- In the User Account Control dialog that opens, click Yes.
A new window opens.

- Double-click Computer Management to open it.
- In the User Account Control dialog that opens, click Yes.
The Computer Management window opens.

- From the navigation pane on the left, select Local Users and Groups.

- Right-click the Users folder and select New User....
The New User dialog opens.

- In the New User dialog:
- In User name, enter a username.
- In Full name, enter the full name of the user.
- In Description, enter a description for the user.
- In Password, enter a password.
- In Confirm password, enter the password again to confirm.
- Click Create to create the user.
- Double-click the Users folder, right-click the user that was created in step 8, and select Properties.
- In the new dialog that opens, go to the Member Of tab, select Administrators, and click Add....
- Click OK to save changes.

If you intend to retrieve RDP logs for the privileged account, you must create a secret for the privileged account with a Windows target. See Creating a secret.

