FortiGate-7000 high availability
FortiGate-7000 supports a variation of active-passive FortiGate Clustering Protocol (FGCP) high availability (HA) between two identical FortiGate-7000s. With active-passive FortiGate-7000 HA, you create redundant network connections to two identical FortiGate-7000s and add redundant HA heartbeat connections. Then you configure each FortiGate-7000 for HA.The FGCP forms a cluster and selects a primary FortiGate-7000. You can set device priorities and enable override to select the primary FortiGate-7000.
Example FortiGate-7040 HA configuration
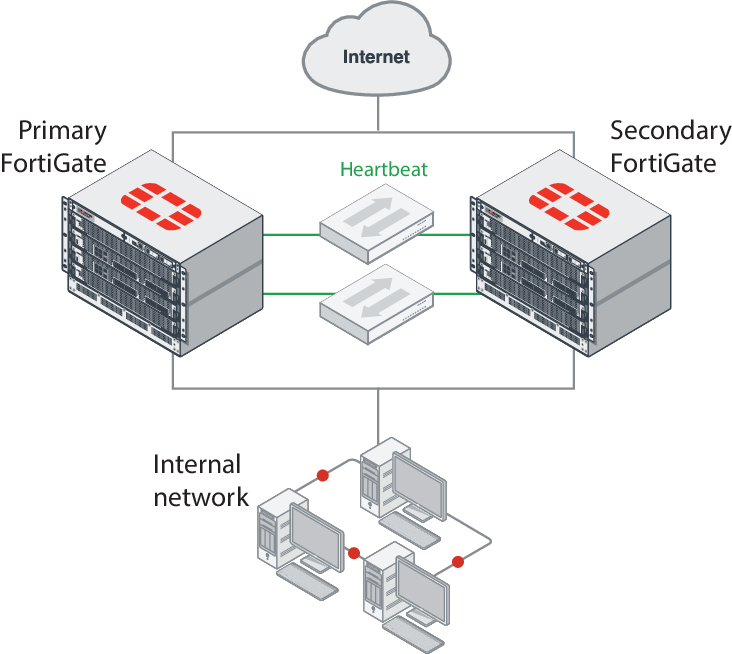
The primary FortiGate-7000 processes all traffic. The secondary FortiGate-7000 operates in hot standby mode. The FGCP synchronizes the configuration, active sessions, routing information, and so on to the secondary FortiGate-7000. If the primary FortiGate-7000 fails, traffic automatically fails over to the secondary FortiGate-7000.
New HA features and changes
Configuring FortiGate-7000 HA has been simplified for FortiOS 5.6.6. To set up HA, you no longer have to configure HA settings for both of the FIMs in a FortiGate-7000. Instead, you configure HA settings on the primary FIM and this configuration is synchronized to the other FIM.
As well, FortiGate-7000 HA is configured and operates more like standard FGCP HA. The link failure threshold concept that was part of FortiGate-7000 for FortiOS 5.4 has been removed and board failover tolerance has been simplified. As well, primary unit selection has been simplified to be more like FGCP primary unit selection.
FortiOS 5.6.6 also includes the following new features and changes:
- The System > HA GUI page now appears and can be used to configure most HA settings.
- You can configure HA interface monitoring (or port monitoring) to detect link failures.
- You can configure HA remote link failover (also called remote IP monitoring) to detect remote link failures using the following options:
- Enable remote IP monitoring with the
pingserver-monitor-interfaceoption. - Set the remote IP monitoring failover threshold with the
pingserver-failover-thresholdoption. - Force the cluster to negotiate after a remote IP monitoring failover with the
pingserver-slave-force-resetoption. - Adjust the time to wait in minutes before renegotiating after a remote IP monitoring failover with the
pingserver-flip-timeoutoption.
- Enable remote IP monitoring with the
- You can use the
get system ha statuscommand to display HA status. Thediagnose sys ha statuscommand is no longer available. - The
diagnose sys ha force-slave-statecommand is no longer available. To force the primary FortiGate-7000 into a secondary (or slave) state you can use thediagnose sys ha reset-uptimecommand. - The HA
link-failure-thresholdoption has been removed. - The
board-failover-toleranceoption has been simplified and determines how the cluster responds to failed FIMs.

