vMotion in a VMware environment
This guide provides sample configuration of a vMotion FortiManager-VM in a VMware environment. VMware vMotion enables the live migration of a running FortiManager-VM from one physical server to another with zero downtime, continuous service availability, and complete transaction integrity. It also provides transparency to users.
The following depicts the network topology for this sample deployment. In this sample deployment, there are two hosts, Host 48 (100.64.30.48) and Host 50 (100.64.30.50), that are members of Cluster 1 in the DataCenter 1. The vCenter server (vcenter67.fmg.lab) manages DataCenter 1.

This configuration requires the following prerequisites:
- You have set up the vCenter server and created the data center and cluster.
- Host 48 and Host 50 are members of the cluster.
- A Gigabit Ethernet network interface card with a VMkernel port enabled for vMotion exists on both ESXi hosts.
- A FortiManager-VM that is set up and able to handle traffic.
To migrate the FortiManager-VM on the vCenter web portal:
- Log in to the vCenter web portal.
- Verify the current location of the FortiManager-VM:
- Go to the FortiManager-VM.
- On the Summary tab, check the Host. In this example, the host is currently Host 48 (100.64.30.48).

- Go to Storage > Files. Check that the FortiManager-VM is located in the correct datastore. In this example, the datastore is currently Datastore 48, in Host 48.
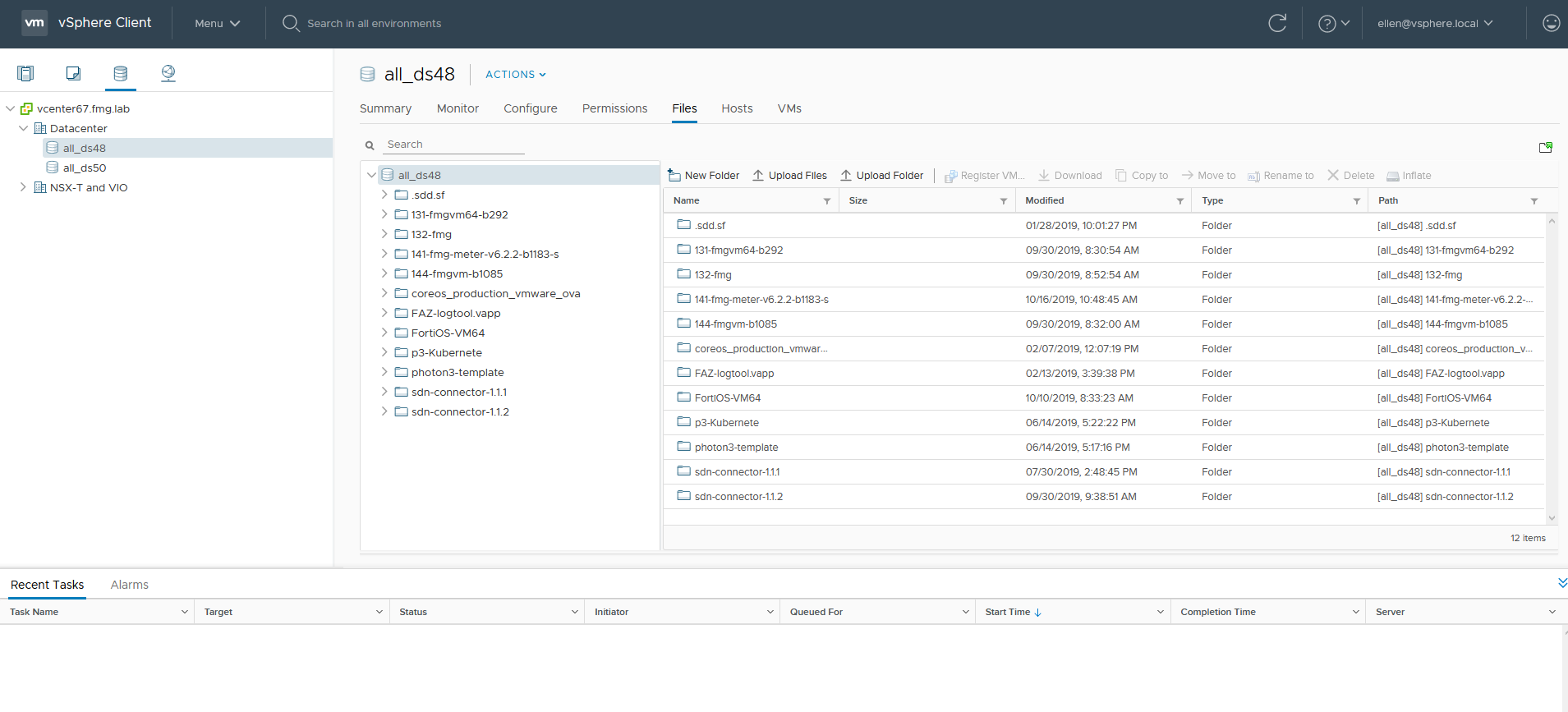
- Right-click the FortiManager-VM and select Migrate.
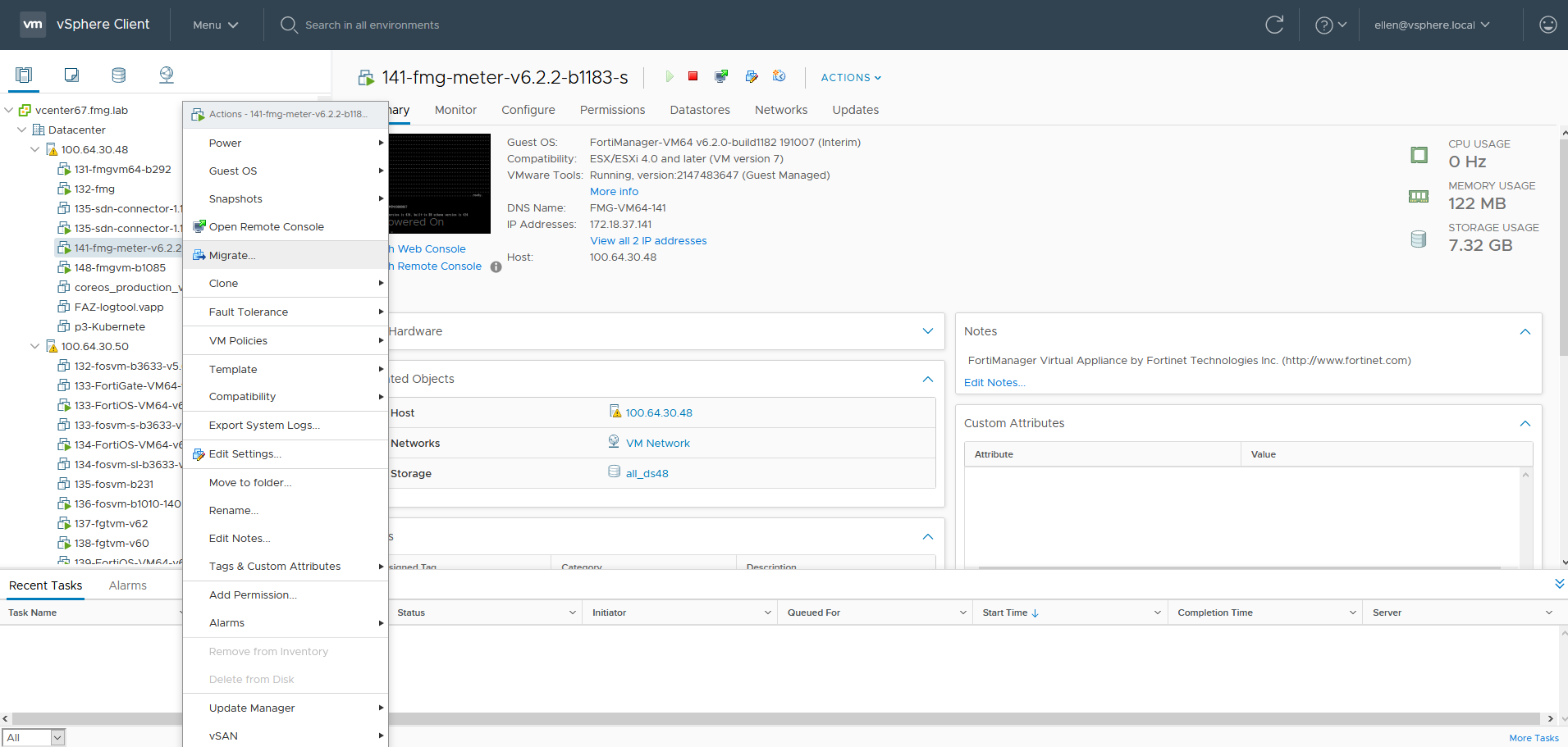
- Configure the migration options:
- For Select a migration type, select Change both compute resource and storage. Click NEXT.

- For Select a compute resource, select the desired new compute resource. In this example, Host 50 (100.64.30.50) is selected. Click NEXT.
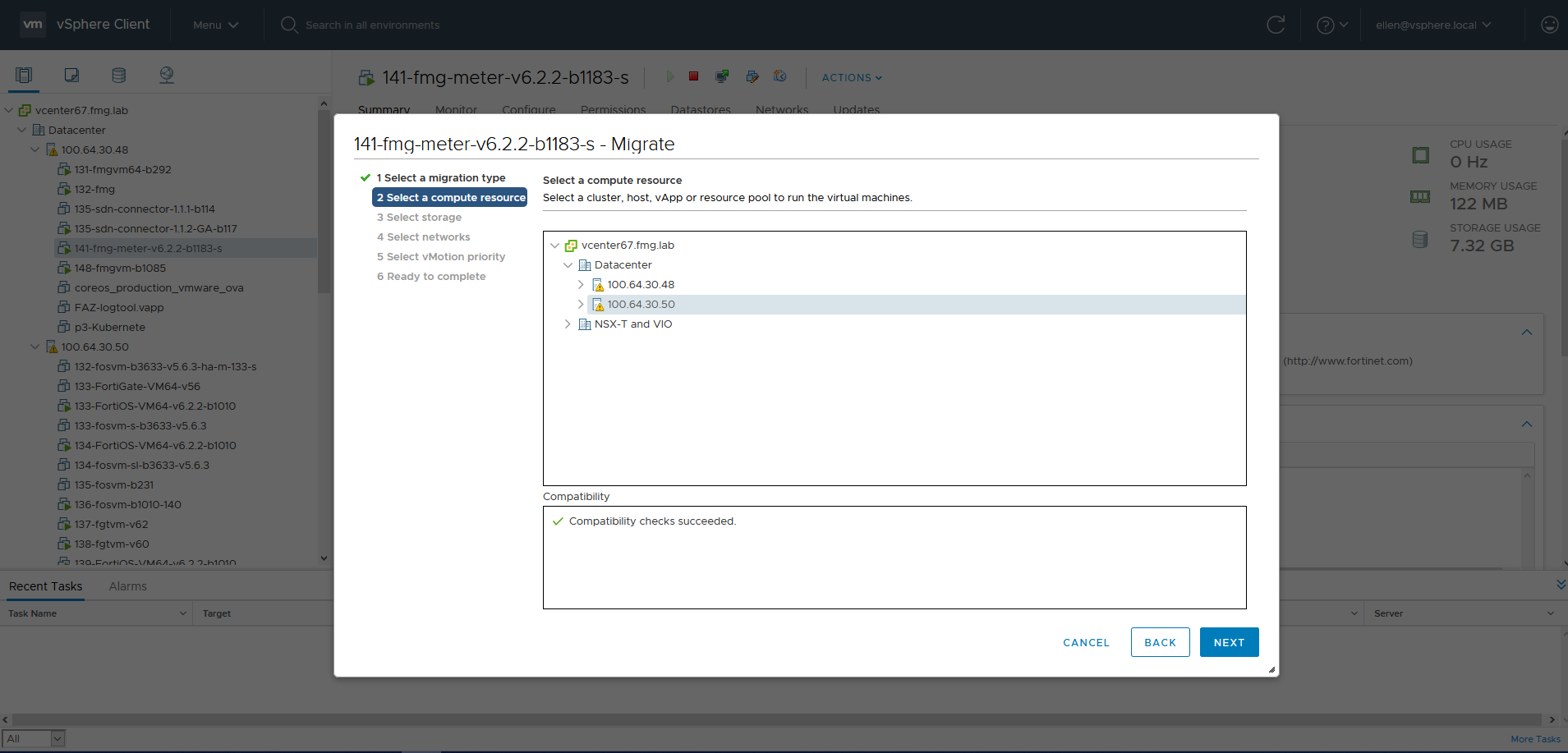
- For Select storage, select the storage associated with the selected compute resource. In this example, Datastore 50 (as corresponds to Host 50) is selected. Click NEXT.
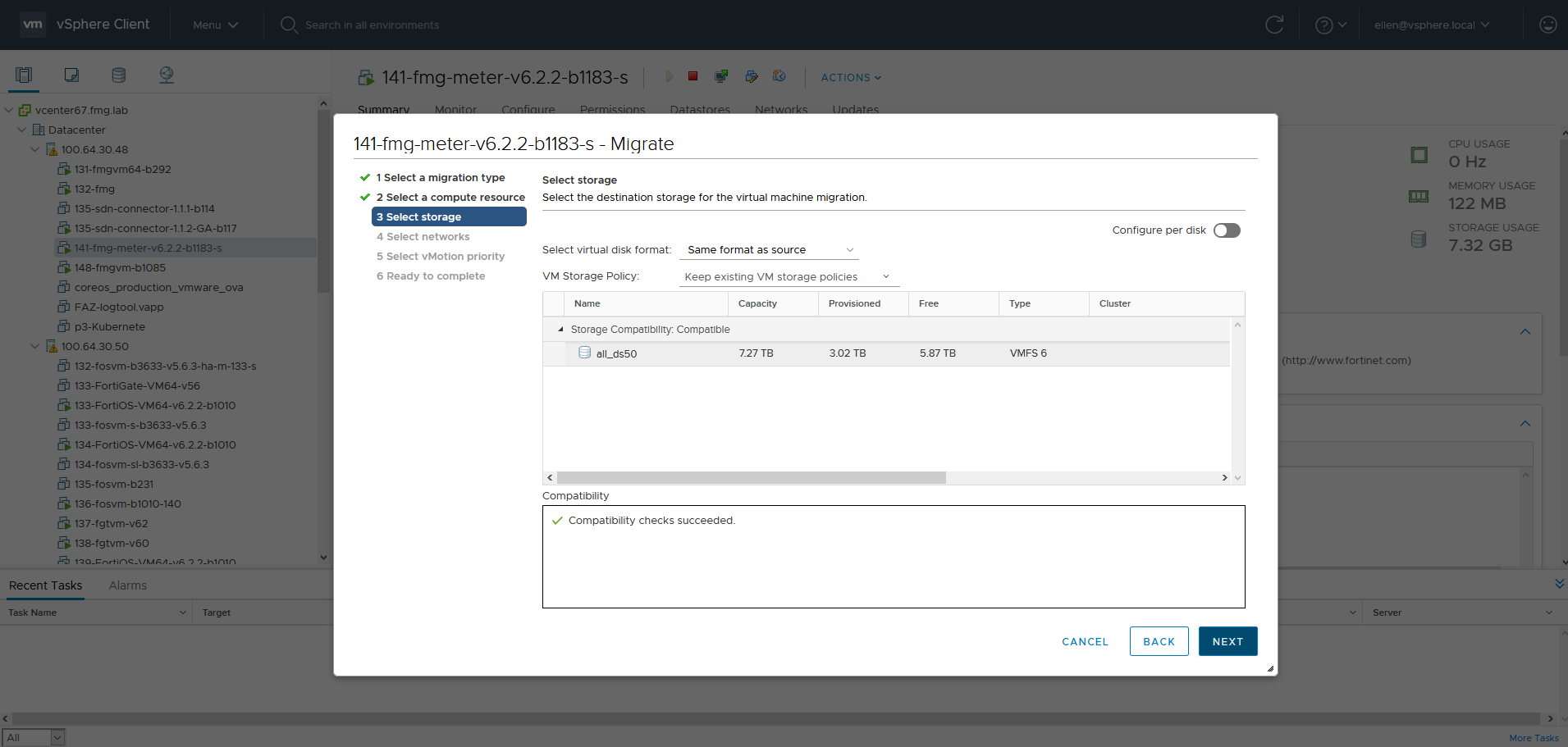
- For Select networks, select the desired destination network at the selected compute resource. In this example, the source network is at Host 48, and the destination network is at Host 50. Click NEXT.
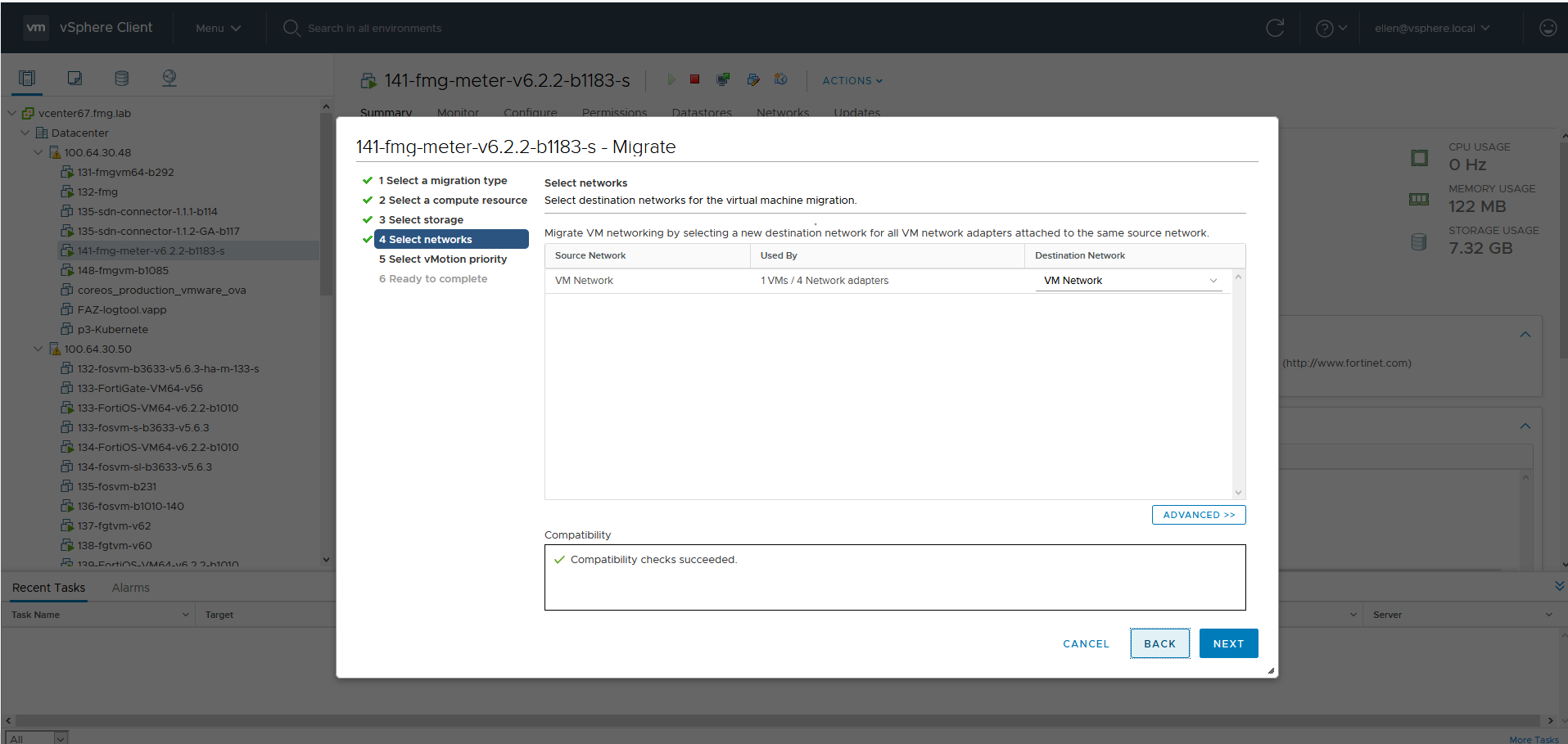
- For Select vMotion priority, select Schedule vMotion with high priority (recommended). Click NEXT.
- For Select a migration type, select Change both compute resource and storage. Click NEXT.
- Before initiating the migration, open the CLI for the FortiManager-VM to check on traffic during the migration. Enter
diagnose sniffer packet any 'icmp and host 8.8.8.8'to check if traffic is stable.If no traffic is lost during migration and the FortiManager-VM SSH session does not break, the output resembles the following: 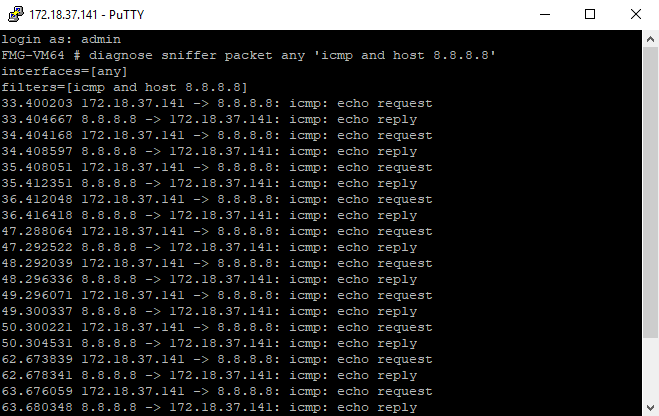
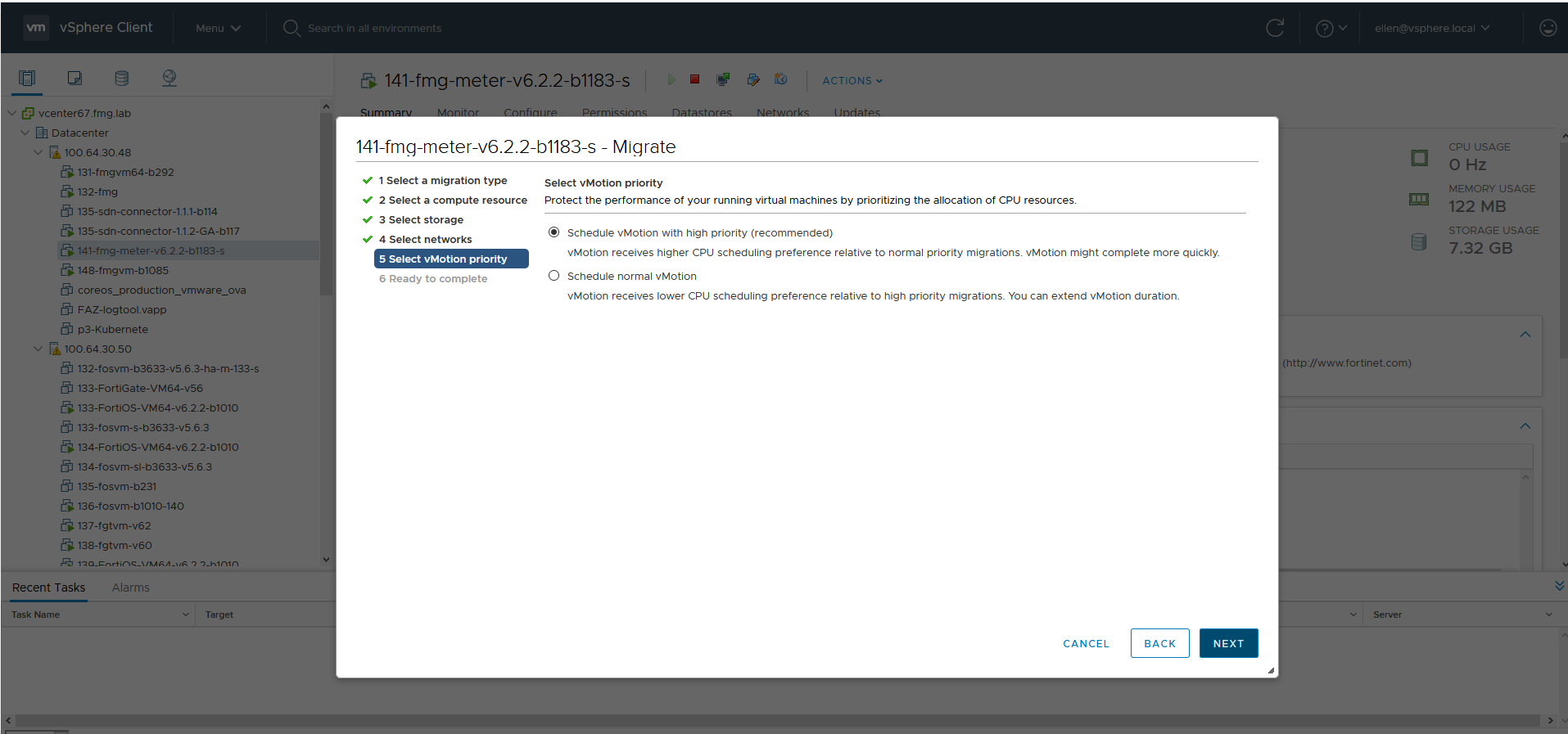
- Click FINISH.
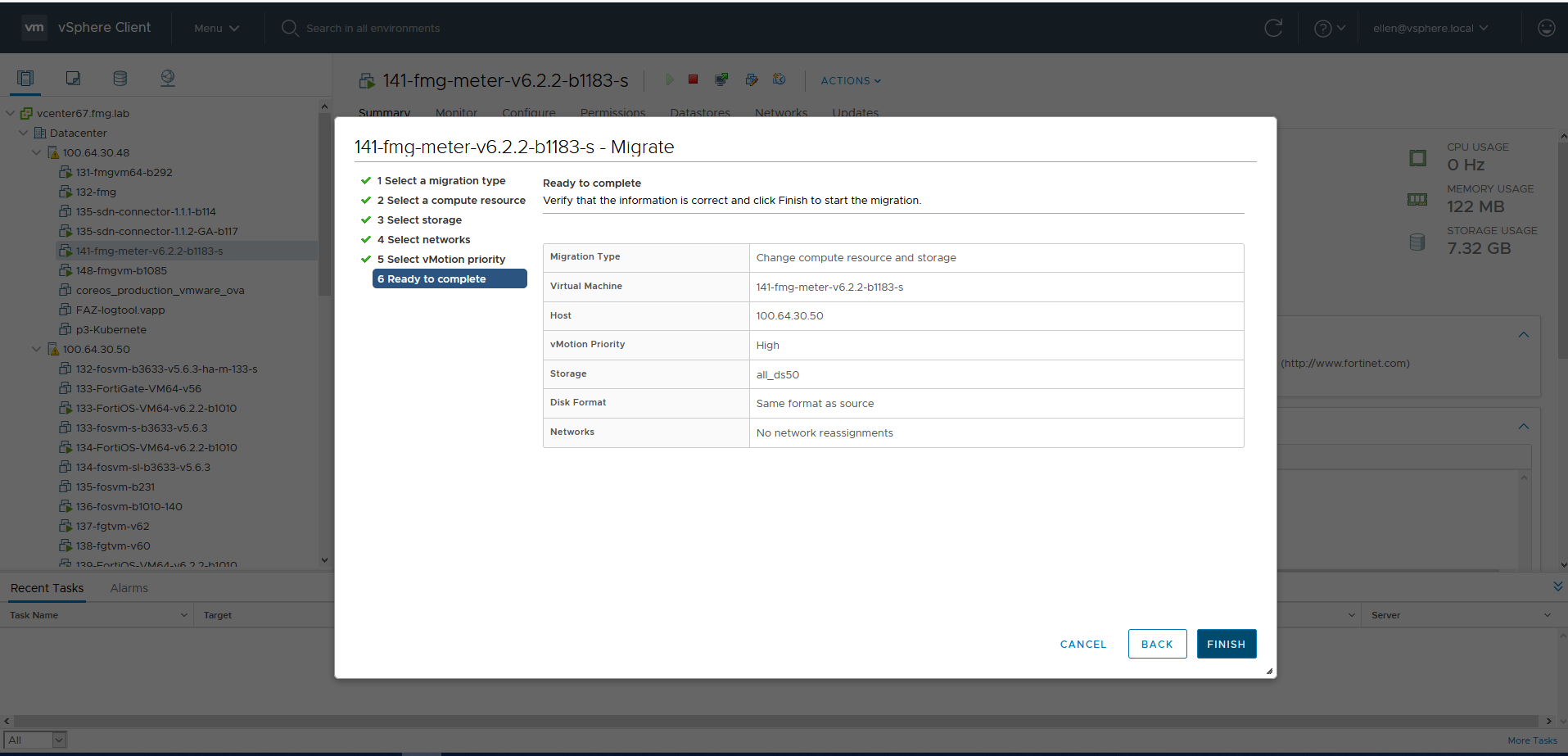
After a few seconds, the FortiManager-VM is migrated to the new compute resources, in this case Host 50.
- Log into the vCenter web portal. Go to the FortiManager-VM. On the Summary tab, the Host is now the new compute resources, in this case Host 50 (100.64.30.50).

- Go to Storage > Files. It shows that the FortiManager-VM is now located in a new datastore, in this example Datastore 50.

