Introduction
This document provides the following information for FortiInsight version 6.4.0:
- What's new in FortiInsight Cloud version 6.4.0
- Upgrade information
- Product integration and support
- Resolved issues
- Known issues
What's new in FortiInsight Cloud version 6.4.0
The following table lists new features and enhancements in FortiInsight Cloud version 6.4.0.
- Improved Default State
- AP V2 Release
- Support More Deployment Regions
- Search Bar Tutorials
- File Printed View
- Threat Hunting Quick View
- Default sort applied to all tables
- Automatic concatenation of search pills
Improved Default State - Out of the Box Policies, and Collections
FortiInsight has increased the number of default policies and collections that are provided out of the box. These are focused around some of the new features made on the FortiInsight Windows Endpoint, including new File Printed events and Command Line Arguments.
New default policies
|
Policy |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Alternate Data Stream Usage |
Alerts on potential code execution or file download using Alternate Data Streams. In Windows systems an ADS is a file attribute which allows storage of additional, possibly malicious, data within files. Using ADSs might aid malicious activity to evade regular detection mechanisms and should therefore be monitored. |
|
Cached Credentials (Without Passwords) Listed |
Alerts on the usage of cmdkey.exe to list cached credentials. While this does not provide passwords, it might be an indicator of reconnaissance being done on the system and should be investigated. |
|
Connection Manager Service Profile Tampering |
Alerts on cmstp.exe which installs or removes a Connection Manager service profile. This should not be used if a VPN is not in use. |
|
File Downloaded Through a LOLBAS Binary |
Alerts on events of LOLBAS binaries being used to download files. LOLBAS stands for Living Off the Land Binaries and Scripts and refers to a group of Microsoft-native legitimate applications which have the potential to be misused, eg to download malware from the Internet. That's why these alerts should be reviewed manually. |
|
Malicious Powershell Execution |
Alerts on Powershell instances started with suspicious command line arguments, such as inline script script execution. These actions could potentially be malicious, regardless if completed manually or automatically by malware. |
|
Ncat or Nc Listener Set Up |
Alerts on an ncat / nc listener being set up using either ncat -l or nc -l commands. This can provide direct access to the machine running the listener and is therefore considered malicious. |
|
Nmap TCP ACK Scan |
Alerts on an attempted or completed nmap TCP ACK scan. Nmap is a reconnaissance tool used to discover open ports and services running on a host and supports various types of scans. The TCP ACK scan is used not to determine whether ports are open or closed, but to map out the firewall ruleset: identify if they are stateful and discover which ports are filtered. This may indicate a malicious user gathering information about the network. |
|
Nmap TCP Connect Scan |
Alerts on an attempted or completed nmap TCP Connect scan. Nmap is a reconnaissance tool used to discover open ports and services running on a host and supports various types of scans. The TCP Connect scan is commonly used when the SYN scan is not an option; that is when nmap does not have raw packet privileges and the operating system is used to make the connection instead. This might be a sign of a deliberate information gathering about the network. |
|
Nmap TCP SYN Scan |
Alerts on an attempted or completed nmap TCP SYN scan. Nmap is a reconnaissance tool used to discover open ports and services running on a host and supports various types of scans. The TCP SYN scan does not complete a full TCP handshake and is therefore stealthy and relatively fast; it is also the most popular scan type. An nmap scan detected might be a sign of a deliberate information gathering about the network. |
|
Nmap UDP Scan |
Alerts on an attempted or completed nmap UDP scan. Nmap is a reconnaissance tool used to discover open ports and services running on a host and supports various types of scans. The UDP scan is used to identify ports with exploitable UDP services. An nmap scan detected might be a sign of a deliberate information gathering about the network. |
|
Powershell Executed On All Machines In Domain |
Alerts on Powershell being used to execute commands on all machines in the current domain. This action can be completed legitimately, but the magnitude of the possible impact makes it worth reviewing. |
|
Scheduled Task Created |
Alerts on scheduled tasks being created. Scheduled tasks have legitimate uses but in case of malware can be an indicator of lateral movement in your system and an attempt at persistence. This is why these flagged events should be monitored and reviewed. |
|
Torrent Client Usage |
Alerts on the usage of known torrent clients, or the presence of torrent files on an endpoint. Torrent clients are commonly used for media piracy, which might be a violation of company policy. |
|
VPN Usage |
Alerts on known VPN clients being executed on an endpoint. Depending on corporate policy and the VPN client used this might constitute a data leak risk. It is advisable to review available VPN software and choose specific products that match your risk appetite and internal policies to manage this risk. |
API V2 GA Release
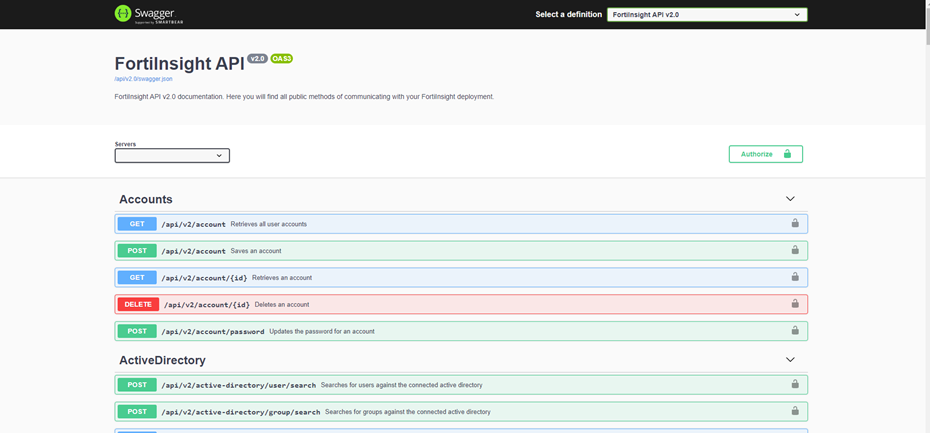
This release introduces FortiInsight API v2, providing additional API functionality. APIv2 documentation is also improved with a new API explorer.- allowing you to build out further integration with other providers such as your favourite SIEMs. Under API Explorer you will find an easy to understand guide for all the API Endpoints that are supported by FortiInsight (including Policy Alerts, LiveEvents, AI Alerts). Based on Swagger, you have the ability to Try Out requests within the API Explorer.
API version 2 also standardizes the API format on all endpoints and responses, making it even easier to integrate with third party systems.
Expanded Available Deployment Regions
FortiInsight can now be deployed in different regions across the globe for greater deployment flexibility and choice of cloud data location.. Previously EU-West-1 (Ireland) was the only supported region. Now FortiInsight supports the following regions as a default deployment option:
- US-East-1 (N.VIrginia)
- US-West-1 (N.California)
- AP-southeast-2 (Sydney)
- AP-northeast-2 (Seoul)
- AP-northeast-3 (Osaka)
- CA-central-1 (Canada Central)
The region choice is made at the time of initial system deployment. It is not possible to transfer FortiInsight between regions. The region must be carefully selected at deployment time, it cannot be subsequently changed.
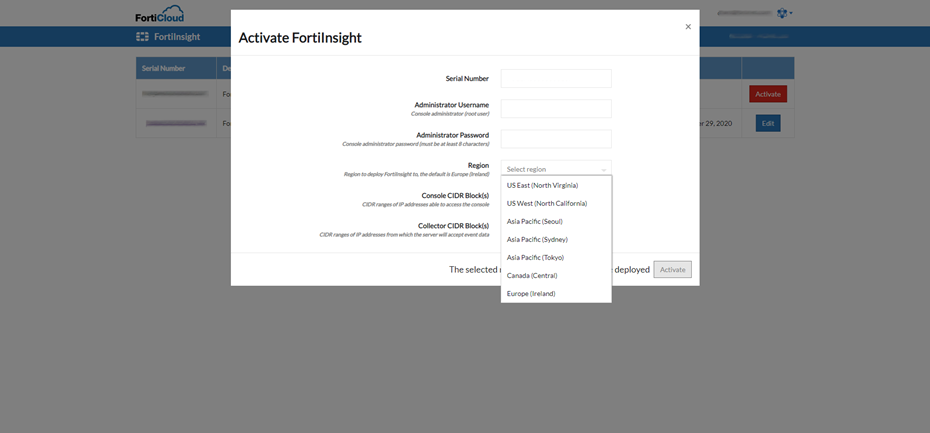
Now you can select any of 7 regions to deploy into.
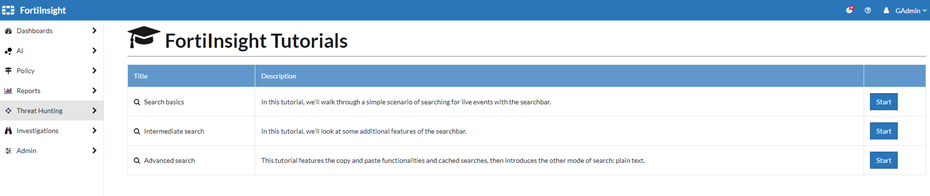
Searchbar Tutorials
FortiInsight 6.4 includes three simple and engaging Searchbar tutorials. These cover the Basic, Intermediate and more Advanced use cases that the Searchbar can utilise. Tutorials are easy to follow step by step interactive guides to aid threat hunting, and searching across the platform in general.


File Printed View
A new File printed activity view is available under the Threat Hunting > Printed section. This data is now, by default, stored for 1 year and allows you to search across all of this activity quickly and efficiently.

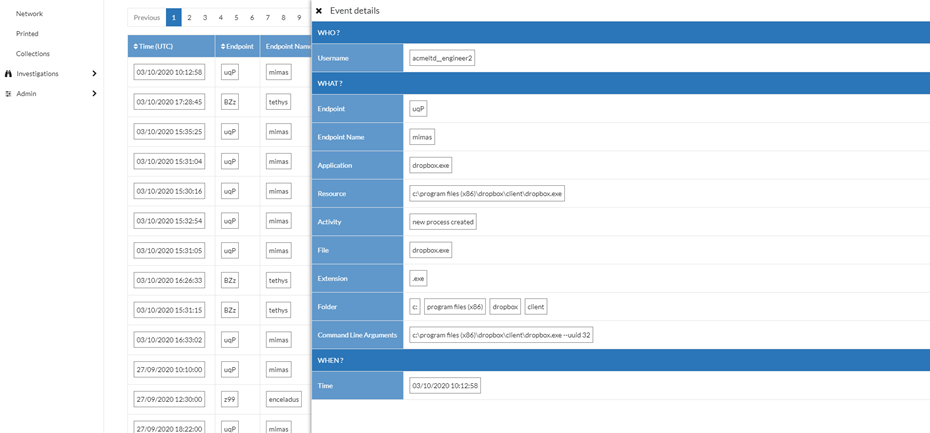
Threat Hunting Quick View
Threat Hunting quick view is now available on all Threat Hunting associated tables, including Live, Compacted, Printed and Network. Here you can select a row, to view all the information on the event. Making it much easier to get to the pertinent data and information while Threat Hunting.
Default Sort on Tables
Now, all tables across the FortiInsight Console, where Time is a supported column, will default to sort by time allowing you to see the latest information first before delving into more details. This feature is supported across Threat Hunting, Policy > Alerts and Ai > Alerts.
Automatic concatenation of search pills
The search bar will now automatically concatenate search pills . Instead of having to manually add the join between the two pills FortiInsight now provides a default ‘AND’. This feature is only available on the Design mode search bar to help you quickly and more efficiently threat hunt across the platform.
For more information about new features, see the FortiInsight Administration Guide.
System requirements
To successfully install and use FortiInsight version 6.4.0, your system must meet the following requirements.
|
Component |
Requirements |
|---|---|
|
Endpoint agent support |
FortiInsight provides endpoint agents for the following platforms:
|
|
Endpoint computers |
|
|
Browser |
Other web browsers may work correctly, but FortInsight does not support them. |
|
Input devices |
The FortiInsight UI is not optimized to use with touch devices. We recommend using a keyboard and mouse as the input devices for interacting with the UI. |
Related resources
The following resources provide more information about FortiInsight:

