FortiExtender and FortiGate integration
FortiExtender works as an extended WAN interface in IP pass-through mode.
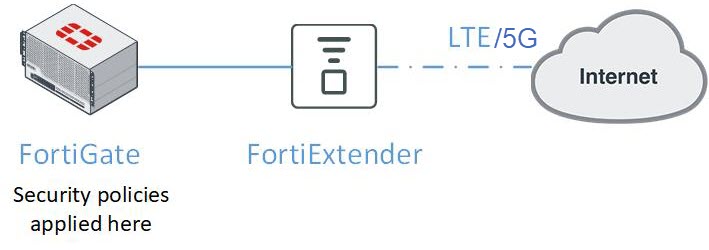
The following paragraphs highlight the network topology for integrating FortiExtender with FortiGate.
In this scenario, FortiGate manages FortiExtender over the Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) protocol in IP pass-through mode. Unlike a standalone 3G/4G/5G wireless WAN extender, the FortiExtender managed by FortiGate integrates directly into the FortiGate Connected UTM (Unified Threat Management) and is managed from the familiar FortiOS interface. This not only enables security policies to be seamlessly applied to FortiExtender, but also provides visibility to the performance and data usage of the connection.
In this scenario, you can connect a FortiExtender to two FortiGate devices for a high availability (HA) configuration in Active-Passive, and two FortiExtenders to two FortiGate devices in Active-Active deployments, providing dual active redundancy for wireless WAN access as well.
FortiExtender and FortiGate share the same LTE IP in WAN-extension mode. In pre-4.2.2 releases, FortiExtender does not allow access to ssh/https/http/telnet service via the LTE interface, so all the traffic to those default service goes to FortiGate. FortiExtender 4.2.2 adds local ssh/https/telnet/http service support via the LTE interface. To distinguish local services from FortiGate services, you must configure FortiExtender to use different ports. Otherwise, all traffic to these default services will be sent to FortiExtender locally instead of FortiGate.
To configure FortiExtender local ssh/https/http/telnet service support via the LTE interface:
config system management
config local-access
set https 22443
set ssh 2222
end
end

