LDAP authentication
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) authentication is an open, industry-standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an IP network. LDAP provides a central place to store usernames and passwords. This enables many different applications and services to connect to an LDAP server to validate users. This has a major benefit that allows a central place to update and change user passwords.
When LDAP authentication is enabled in FortiEDR, whenever a user attempts to log in to FortiEDR, the system looks for that user name and password in the central directory, instead of within the FortiEDR directory. If the user is not found on the LDAP server, the system checks whether the user is defined locally (under Administration > Users > Local Users).
Before you start firewall configuration, make sure that your FortiEDR deployment includes an on-premise Core that has connectivity to the LDAP server. Details about how to install a FortiEDR on-premise Core can be found in Setting up a FortiEDR Core as a Jumpbox.
To set up LDAP authentication in FortiEDR:
- Click the LDAP AUTHENTICATION button.

The following window displays:
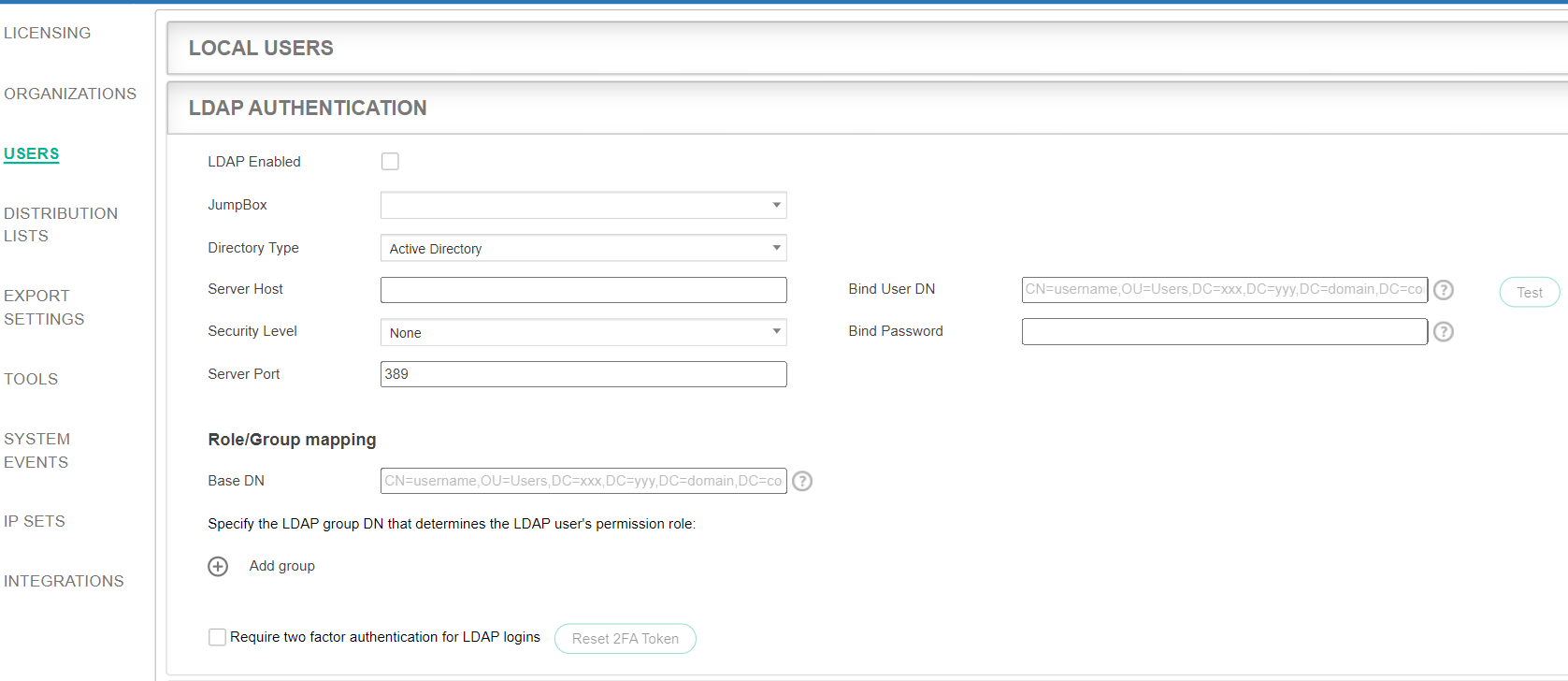
- Fill in the following fields:
Field
Definition
LDAP Enabled Check this checkbox to enable LDAP authentication in FortiEDR. JumpBox Select the FortiEDR Core to communicate with the LDAP server. Only FortiEDR Cores configured with JumpBox functionality appear in the list. If no such core exists in the system, the list is empty and FortiEDR displays a warning message. Directory Type Specify the type of central directory in use. FortiEDR supports Active Directory and OpenLDAP. The default is Active Directory. Server Host Specify the IP address of your LDAP server. Security Level Specify the protocol to be used for the secured connection: TLS, SSL, or None. Server Port This value is dependent on the security protocol that was selected. Bind User DN/Bind Password
Specify the user and password for the authentication of FortiEDR in the Central Directory.
Role/Group mapping Specify the base DN and define group/role mapping and permissions of the group:
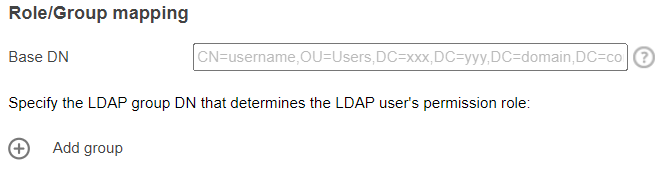
- In Base DN, specify the location in the Central Directory hierarchy where the Groups that are used for permission mapping can be found. For example, the DN for the root of the domain should always work, but results in low performance.
- Click Add group.
- Define group/role mapping and permissions of the group:
- In the Group field, specify the name of the group, as it is defined in your central directory (Active Directory or OpenLDAP), that is to be granted FortiEDR permissions. You can specify multiple groups in this field by separating them with commas. For example,
group_name1, group_name2. - Under Role, select a role from the list. See Users for more information about the roles.
- Under Advanced, enable any additional privileges for the group. Some options are role-dependent.
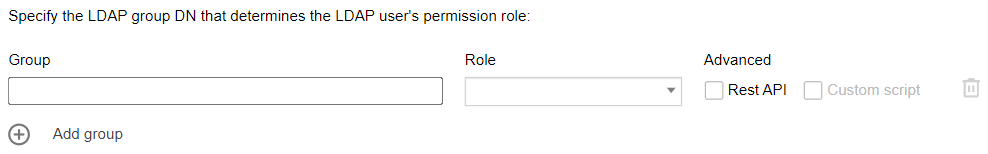
- In the Group field, specify the name of the group, as it is defined in your central directory (Active Directory or OpenLDAP), that is to be granted FortiEDR permissions. You can specify multiple groups in this field by separating them with commas. For example,
- Click Add group and repeat step 2 for each role you want to map to a group or multiple groups.
For example:
To give the user John Admin permissions in FortiEDR (for both the FortiEDR application and the RESTful APIs), assign John to a FortiEDRUsers group that is defined in your Central Directory:
- Specify
FortiEDRUsersunder Group. - Select Admin under Role.
- Check the Rest API checkbox under Advanced.
During authentication, FortiEDR determines the relevant role for the user John by checking that the Central Directory exists and that the password used in the FortiEDR login page matches the password in the Central Directory. If both exist and are correct, then FortiEDR checks the FortiEDRUsers group to which John is assigned and in this case, and matches the user role permissions.
- If users must use two-factor authentication to log in, check the Require two-factor authentication for LDAP logins checkbox. For more details about two-factor login, see the Two-factor Authentication section in Two-factor authentication.

Click the Reset 2FA Token button to reset the two-factor authentication token for a specific user. This process works in the same way as described in Resetting a user password.
- Click Save.

Users in Active Directory must not have a backslash (\) in the user name, in order for the name be supported by the FortiEDR Console. In some cases in Active Directory, a backslash is added when there is a space between a user’s first and last names. For example,
CN=Yell\,.

