Agent configuration
Once installed the FortiAuthenticator Agent Configuration utility will automatically open. This can also be started via the Start menu.
To configure FortiAuthenticator Agent for Microsoft Windows:
- Launch the FortiAuthenticator Agent for Microsoft Windows.

- Select the General tab, and click the Two Factor Authentication > Configure button.

The Simulation tab, shown in the image below, is used for the testing of the login process and is not used in normal operation.

- In the Two Factor Authentication configuration screen, configure the IP address, username and API key obtained in FortiAuthenticator Configuration. See FortiAuthenticator configuration.
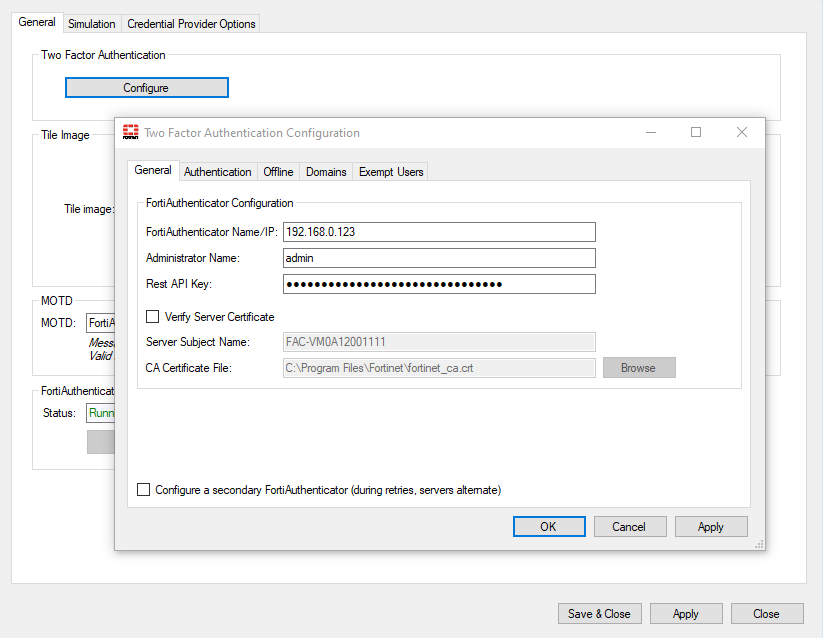
- For test purposes, disable Verify Server Certificate. This can be configured once the installation has been tested and proven working.

If there is a server subject name or CA certificate file specified, enable Verify Server Certificate, delete the entries and disable Verify Server Certificate. Authentication may fail in some circumstances if this is not performed.
- Select the Domains tab and select the domains you want to include in the two-factor authentication process by clicking the arrow.

FortiAuthenticator Agent for Microsoft Windows contains the default domain "." which represents the local user. You can disable local user login by including the "." domain in the list of domains included in two factor authentication. When the "." domain is not included, login is enabled for local users.
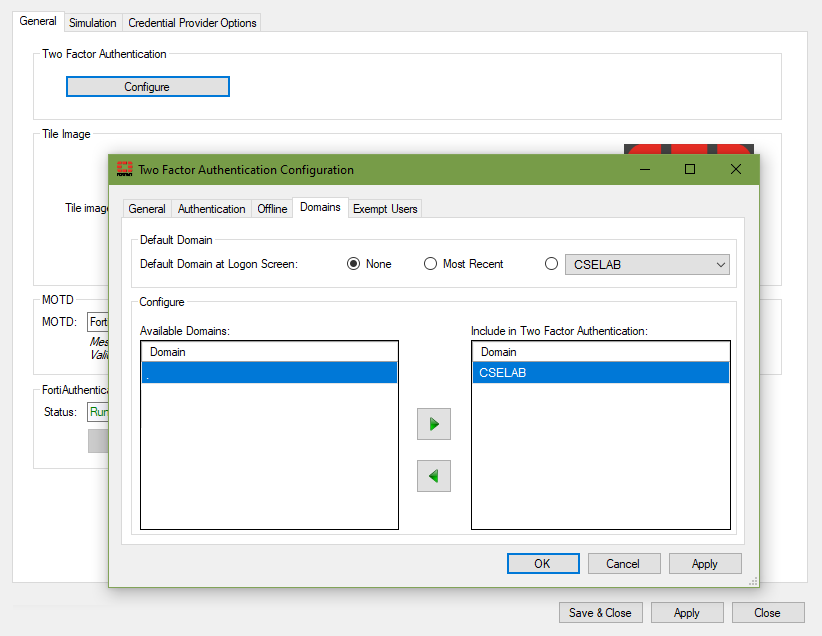
To enable full support for the local PC user:
- Select the General tab, and in Two Factor Authentication select Configure.
- Select the Domains tab, and include the default local domain "." in the Include in Two Factor Authentication list.
Alternatively, use the existing CLI parameter
/INCLUDEDDOMAINS=during installation. - In the FortiAuthenticator server, go to Authentication > User Management > Realms.
- Rename an existing local realm to "." or create a new local realm with the name ".".

Enabling full support for the local PC user requires FortiAuthenticator server 6.4.2 and above. With FortiAuthenticator 6.4.1 and below, FortiAuthenticator Agent for Microsoft Windows shows limited behavior, i.e., the Windows Agent blocks all local users (except exempt local users).

If you want to use push authentication, i.e., mobile, SMS or email push, the user password on the PC and FortiAuthenticator should be the same. In the case of typed-in mobile OTP, the user password on the PC and FortiAuthenticator can be different.
When only FortiAuthenticator Agent for Microsoft Windows configured for local PC user support:
Only step 1 and 2 in To enable full support for the local PC user done.
FortiAuthenticator Agent for Microsoft Windows will only have limited (pre v4.2) support for the local user. The Windows Agent blocks all local users (except exempt local users) even when the Windows Agent is configured to handle "." domain.
When no configuration related to full support for the local PC user is set:
Local users are able to log in to the PC without any token.

