ZTNA Destination
You can use FortiClient to create a secure encrypted connection to protected applications without using VPN. Acting as a local proxy gateway, FortiClient works with the FortiGate application proxy feature to create a secure connection via HTTPS using a certificate received from EMS that includes the FortiClient UID. The FortiGate retrieves the UID to identify the device and check other endpoint information that EMS provides to the FortiGate, which can include other identity and posture information. The FortiGate allows or denies the access as applicable. See Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) for FortiOS configuration requirements. For TCP forwarding to non-web-based applications, you must define ZTNA connection rules in FortiClient as follows.
For Linux devices, ZTNA certificate provisioning requires Trusted Platform Module 2.0.
It is recommended for FortiClient to receive ZTNA destinations from EMS as configured by the EMS administrator. See the FortiClient EMS Administration Guide.
You cannot use ZTNA destinations and TCP forwarding on a Windows 7 endpoint.
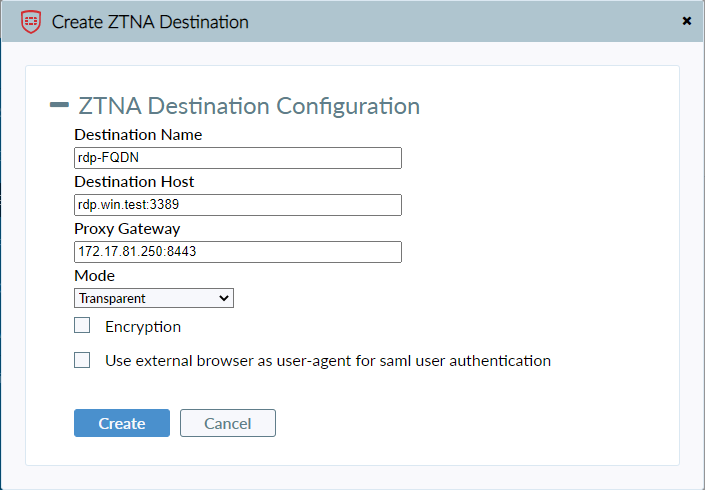
To add a ZTNA destination:
- On the ZTNA Destination tab, click Add Destination.
- In the Destination Name field, enter the desired name.
- In the Destination Host field, enter the IP address/FQDN and port of the destination host in the format <IP address or FQDN>:<port>. This field does not support entering a hostname. For example, you could enter demo.fortinet.com:22 as the destination host value.
- In the Proxy Gateway field, enter the FortiGate access IP address and port in the same format. For example, you could enter 21.14.22.11:80 as the proxy gateway value.
- From the Mode dropdown list, select Transparent.
- Enable or disable Encryption. By default, Encryption is disabled. When Encryption is enabled, traffic between FortiClient and the FortiGate is always encrypted, even if the original traffic has already been encrypted. When Encryption is disabled, traffic between FortiClient and the FortiGate is not encrypted.
- If desired, enable Use external browser as user-agent for saml user authentication. FortiClient can use a browser as an external user-agent to perform SAML authentication.
- Click Create.