1+1 fast failover between FortiGate WiFi controllers
The following shows a simple network topology for this recipe. The primary and secondary FortiGates must be routed into subnets and NAT must not be done on the traffic. The FortiAP must be able to reach both the primary and secondary FortiGates.
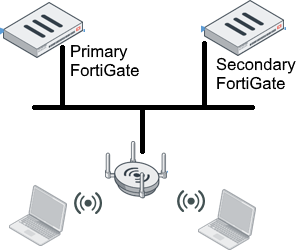
The following takes place in the event of a failover:
- The primary FortiGate syncs the wireless configuration to the secondary FortiGate.
- If the primary FortiGate fails, the secondary FortiGate takes over management of the FortiAP. The client can still connect with the SSID from the FortiAP and pass traffic.
- When the primary FortiGate is back online, it returns to managing the FortiAP.
In the CLI example below, the primary FortiGate has an IP address of 10.43.1.80, and the secondary FortiGate has an IP address of 10.43.1.62.
To configure the primary FortiGate:
config wireless-controller inter-controller
set inter-controller mode 1+1
set inter-controller key 123456
config inter-controller-peer
edit 1
set peer-ip 10.43.1.62
set peer-priority secondary
next
end
To configure the secondary FortiGate:
config wireless-controller inter-controller
set inter-controller mode 1+1
set inter-controller key 123456
set inter-controller-pri secondary
config inter-controller-peer
edit 1
set peer-ip 10.43.1.80
next
end
To run diagnose commands:
- On the primary FortiGate, run the
diagnose wireless-controller wlac -c hacommand. The output should resemble the following:WC fast failover info
cfg iter: 1 (age=17995, size=220729, fp=0x5477e28)
dhcpd_db iter: 123 (age=132, size=1163, fp=0x5435930)
dhcpd_ipmac iter: 123 (age=132, size=2860, fp=0x587d848)
mode: 1+1-ffo
pri: primary
key csum: 0x9c99
max: 10
wait: 10
peer cnt: 1
FWF60E4Q16027198: 10.43.1.62:5245 secondary UP (age=0)
- On the secondary FortiGate, run the
diagnose wireless-controller wlac -c hacommand. The output should resemble the following:WC fast failover info
mode: 1+1-ffo
status: monitoring
pri: secondary
key csum: 0x43e
max: 10
wait: 10
peer cnt: 1
FG22E1T919900557: 10.43.1.80:5246 primary UP (age=0)
dfile 0 iter 1 (age=133, size=1564731/1564731)
dfile 1 iter 1 (age=163, size=0/0)
dfile 2 iter 1 (age=163, size=0/0)
|
|
You cannot use FortiGate Clustering Protocol and Wireless 1+1 fast failover together. They are two different HA features and cannot be combined. |

